Do Men Have Estrogen? Yes, and It's Critical to Their Health
Attention, menfolk: It's time to talk about estrogen. Although is typically associated with women, estrogen is crucial to male health. When men don't have enough, body fat build ups, their libidos dull and they may find that they're unable to perform in bed. When they have too much, however, things can go haywire too. As in all areas of life, maintaining a balance is key.
Read more:
What do testosterone and estrogen do? Testosterone is an androgen, or steroid hormone; in men, androgens trigger the development of reproductive organs — the penis, testes, prostate, etc. Testosterone promotes muscle and bone mass, hair growth, sperm production and sex drive.
Estrogens are typically classified as the female sex hormones. They include estrone, estradiol and estriol. Estrogens cue the development of breasts, pubic hair and underarm hair at puberty. They play a role in menstruation, pregnancy, lactation, blood clotting and sexual function. And they influence mood and are of key importance in bone formation and maintaining bone mass.
How much of each should men have? Normal levels of testosterone and estrogen vary from man to man: average testosterone falls between 260 and 1,000 nanograms for every deciliter of blood. The average estrogen range for men is 10 to 40 picograms for every milliliter of blood. (For reference, a nanogram is a billionth of a gram, whereas a picogram is a trillionth of a gram.) An enzyme called aromatase converts male testosterone into estradiol.
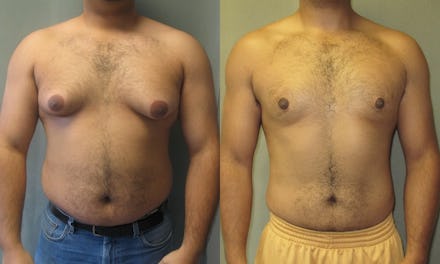
What does too much estrogen do to men? As men age, they produce less and less testosterone: After age 30, testosterone levels drop about 1% annually, eventually leading to andropause, referred to as "male menopause" in popular parlance. As in women, this menopause comes with mood changes, weight gain, difficulty sleeping, hot flashes, depression, night sweats, low libido and hair loss; men will often experience erectile dysfunction and the development of male breasts.
Many of the symptoms of male menopause go along with excess estrogen as well, likely because estrogen levels tend to rise as testosterone levels dip. When estrogen far outweighs testosterone, the health dangers for men begin to pile up.
For example, a 2007 study suggested that an increase in men's estradiol levels increased their risk of stroke. And as LifeExtension reported in 2008, men with coronary artery disease and male heart attack victims tended to have higher estrogen levels and lower testosterone levels.
What does too little estrogen do to men? In 2013, NBC reported on a study by the New England Journal of Medicine. Over the course of 16 weeks, the study looked at 400 men between the ages of 20 and 50, divided into two groups. All the participants took a drug that put the breaks on the production of both testosterone and estrogen; one group was then given testosterone replacement pills, while the other got placebos.
What researchers found was that the group that was taking testosterone but not producing estrogen were subject to erectile dysfunction, decreased in sex drive and increased body fat levels.
And that's not all. Men need estrogen to preserve their bone mass. When they don't get enough, they're more likely to get osteoporosis, whereas their bone density improves with the addition of estrogen.
The bottom line? Balancing estrogen levels is crucial to men's health, as it is to women's. As they age, men should key an eye on their hormone levels and work with their physicians to keep their testosterone and estrogen in line.